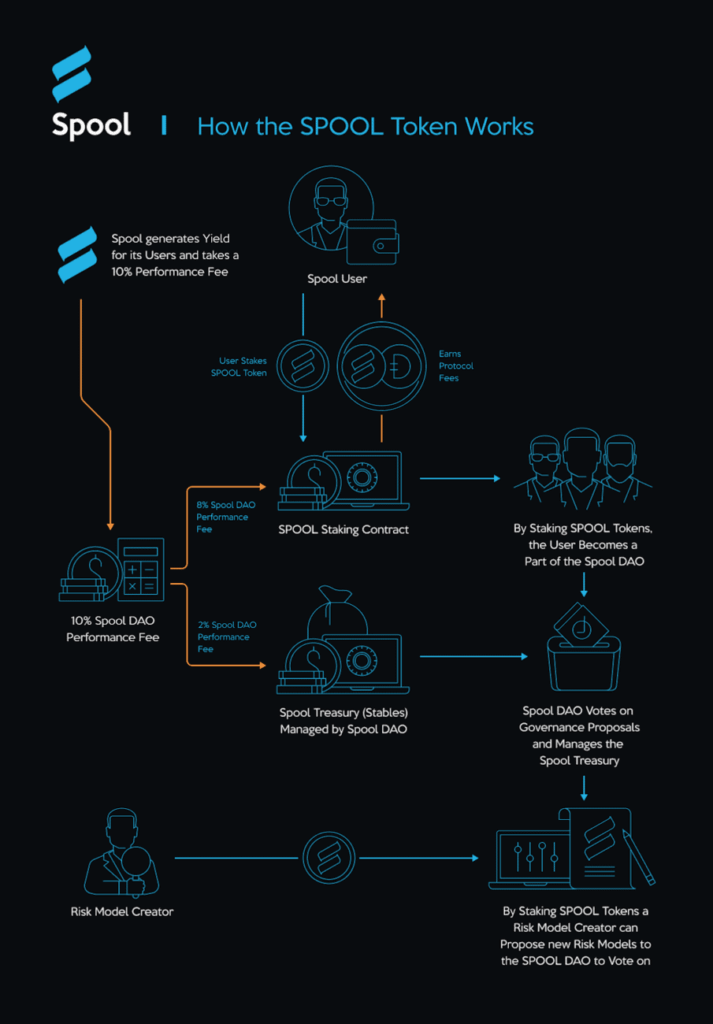
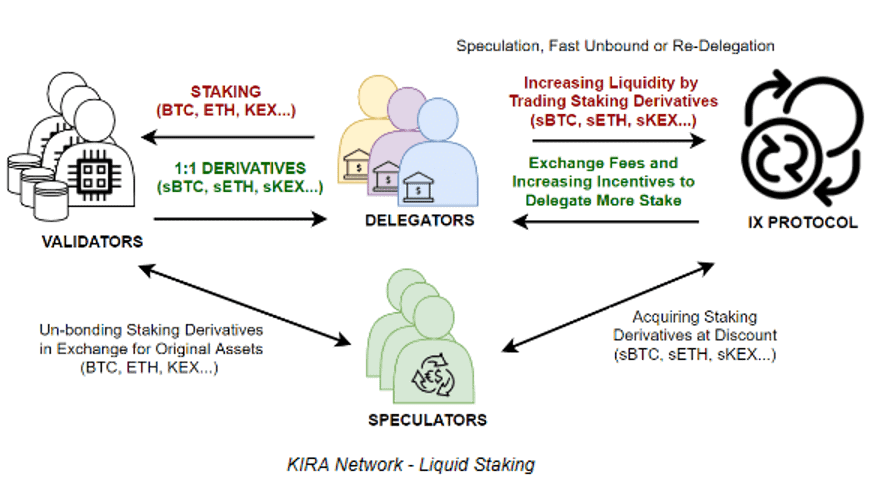
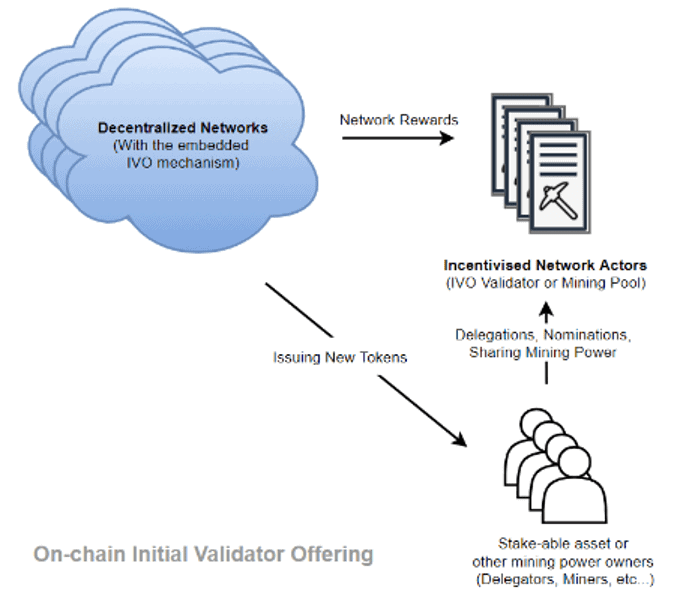
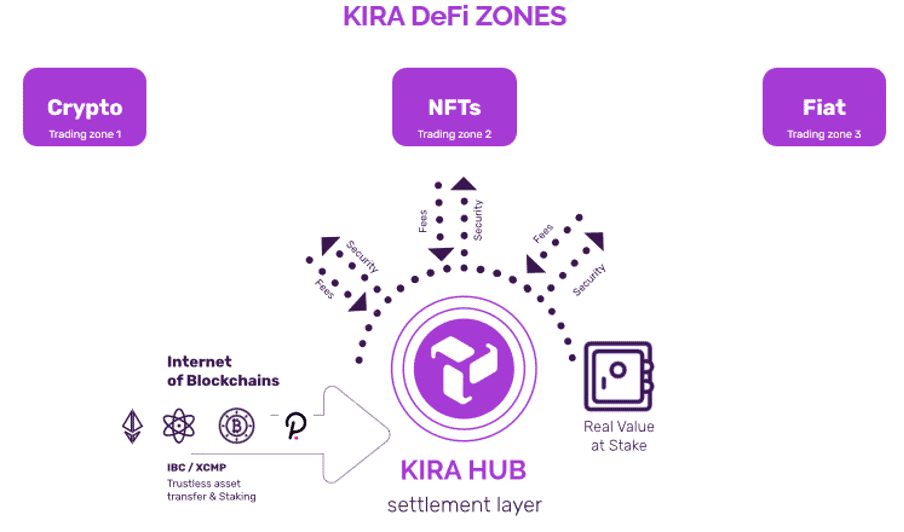
Vortex DeFi ($VTX) aims to provide users a one-stop access to all leading decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and protocols from a single web-based user interface.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has evolved from a niche subcategory to the biggest catalyst driving the cryptocurrency and blockchain field today. It’s primarily focused on the Ethereum network, which has the majority of the DeFi share. There are, however, a large number of core DeFi protocols, combinators, and countless forks. All of this can become confusing fast.
Fortunately, users don’t have to delve into the complex workings and nuances of these protocols, which can be overwhelming even for long-term users. Vortex DeFi is introduced to simplify the access and exposure to the sector. It has integrations with different protocols, which abstracts away the complexity in a simple and yet intuitive interface, to level the playing field and ensure greater participation.
Background
Vortex DeFi launched in Aug 2020 through a private investment round. It accrued interest and funding from X21 Digital, DuckDao, Moonrock Capital, Magnus Capital, Pluto Digital Assets PLC, Faculty Capital, A195 Capital, etc. A public sale will be held soon.
It has a multicultural team, led by CEO Rahul Singh and strategic advisor Lester Lim. The other prominent team members are technical lead Arun Sunil and product lead Shaz. All team members have previous experiences in market-leading companies and blockchain projects.
What is Vortex DeFi?
Vortex DeFi is a web-based DeFi management system or a comprehensive DeFi aggregative solution platform, serving as a bridge between Ethereum and Polkadot. It combines the functionality and power of core protocols in a sleek dashboard to allow users of all categories to engage in yield farming. The core services provided are NFT asset management, lending and borrowing, insurance, and exchange.
Vortex DeFi will also utilize the yEarn finance protocol to access and extract value from various lending protocols to enable automated profitable yield farming. The added advantage of cross-chain compatibility ensures that users don’t have to choose between two promising blockchains. Vortex DEFI also has several components, taking the guesswork and experimentation out of the process.
Vortex DEFI – Components
V-Swap
Being the Uniswap or Bancor equivalent of Vortex, V-Swap will offer an automated digital assets exchange on the Ethereum and Polkadot blockchain. It’s likely to offer liquidity aggregation from multiple sources, so a peer to peer exchange of tokens can be performed without a direct counterparty or orderbook.
V-Pay
It will offer a fiat gateway for users, so they can acquire and sell crypto assets from FIAT, in their cards or bank accounts. This is required for onboarding new users, as well as ensuring that they have a way for realizing their returns.
V-Yield
A yield aggregator as the name goes, V-Yield will combine yield from different sources and optimize them according to the best return rate. It will spare users from the trouble of manually finding sources and having the need to rotate them.
V-NFTs
An asset management, V-NFTs will allow users to manage their asset collection and swap them for each other. Given that NFTs are an illiquid asset class and their infrastructure is scattered, it’s hugely important to develop a unified interface.
V-Insure
DeFi protocols are rife with exploits and smart contract risks. Therefore, to onboard new users and even to retain existing ones, it’s necessary to grant them peace of mind by ensuring the protection of their funds. V-Insure will seek to insure user funds by seeking out integrations with multiple DeFi insurance protocols.
Vortex DEFI Native Token ($VTX)
The native token of the platform is Vortex DeFi Token ($VTX), ERC-20 token, which will be used to incentivize users. It has four purposes:
- Liquidity pools (LP) rewards are distributed in VTX
- Usage for staking on the platform.
- Holding VTX tokens allows users to save on the platform fees
- The team has announced plans to regularly buy tokens and burn them every quarter to reduce supply and increase the value of existing tokens.
All of these benefits and value accrual mechanisms will motivate users to hold tokens, in anticipation of rising demand and prices.
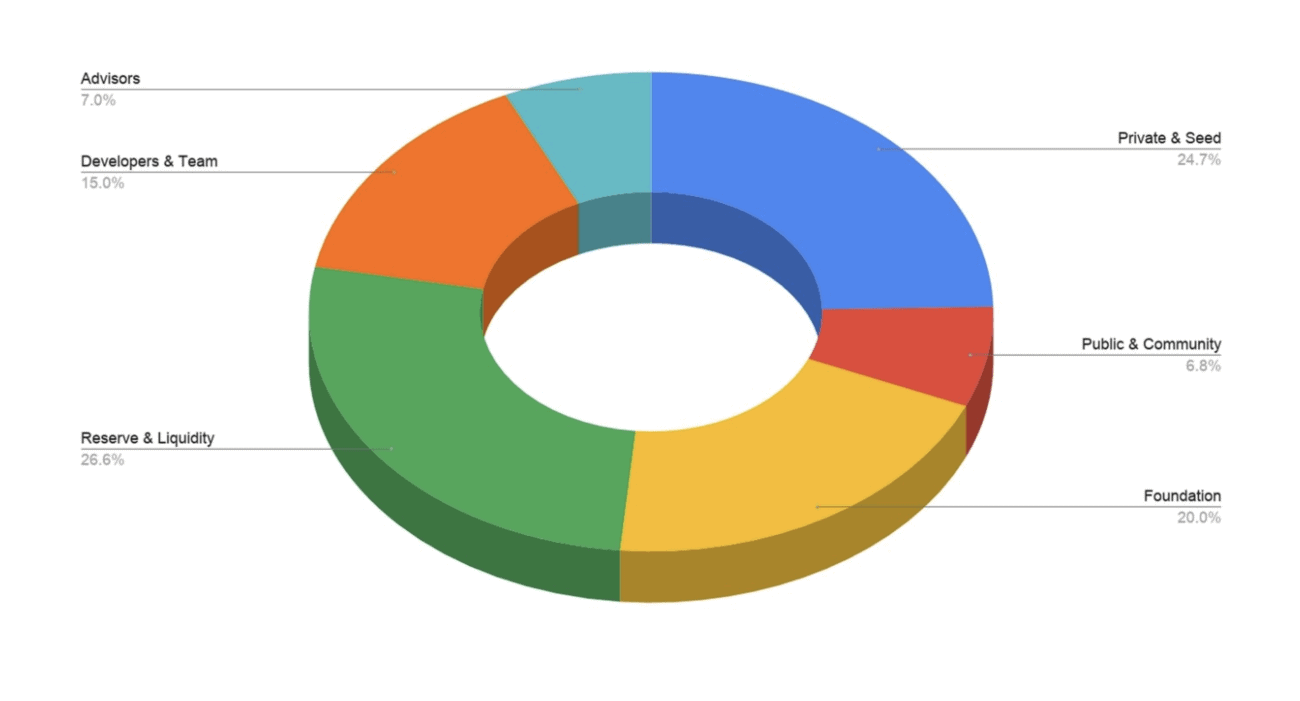
$VTX Token Metrics
The VTX token has a total supply of 100M $VTX and an initial circulating supply of $0.4M $VTX.
Funding Rounds
Private Sale (concluded): 32,500,000 VTX sold at 0.0276 USD per token.(25% TGE, 75% vesting over 120 days)
Public Sale (on 28 February 2021): 2,500,000 VTX to be sold at 0.04 USD per token. No vesting period.*
Advantages of Vortex DeFi
The platform offers users the advantages of a unified DeFi management dashboard, the ability to fuse several protocols together offering a seamless experience with abstracted complexity, powerful lend and earn functionality, automated rotation of funds for optimized returns, non-custodial function, and insurance against loss of funds.
Vortex DEFI Connected Protocols

Vortex DEFI will have integrations with several key DEFI protocols, including but not limited to Maker DAO, Compound, Kava, Idle, Aave, Yearn, Uniswap, Nexus Mutual, Curve. This will allow for a powerful user experience, which is likely to improve penetration of decentralized finance.
Vortex Vision
The team hopes that Vortex will become the top one-stop solution for a user’s DeFi needs and allow them to simplify their experience. Vortex hopes to make financial applications accessible and simple for all users, regardless of their technical expertise. It will also allow saving on transaction fees (gas) by batching and combining transactions.
Vortex can also enhance the decentralization level of DeFi protocols by ensuring broad participation and an increase in user activity. Furthermore, it will feature the DAAS (DeFi-As-A-Service) business model. Currently, the product is in development and more changes are expected as the platform launch draws near.
Conclusion
DEFI was founded on the principle of openness, equal opportunity, transparency, trustlessness, lack of centralized control, fast processing, and lego-like composability. It is generally presented as a superior alternative to the traditional financial system, which differs heavily from the principles of the crypto community and disallows these services to a large number of people.
On the other hand, DeFi is accessible to almost everyone with an internet connection and a personal computing device or smartphone. However, primitive user interfaces and experiences of the existing DeFi protocols were a problem. Thankfully, Vortex will overlap the strong functionality of these protocols with an amazing and simple interface.
Currently, there is a lack of dashboard-style platforms connected to multiple DEFI protocols, aggregating their services and offering a one-stop solution. All of this is about to change with the Vortex launch, which is likely to onboard a large number of new users as well as provide a novel interesting solution to the existing ones.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
With content for both beginners and more advanced users, check out our YouTube DeFi series containing tutorials on the ESSENTIAL TOOLS you need for trading in the DeFi space e.g. MetaMask and Uniswap. As well as a deep dive into popular DeFi topics such as decentralized exchanges, borrowing-lending platforms and NFT marketplaces
The DeFi series on this website also covers topics not explored on YouTube. For an introduction on what is DeFi, check out Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Overview: A guide to the HOTTEST trend in cryptocurrency
Tutorials and guides for the ESSENTIAL DEFI TOOLS:
- MetaMask Guide: How to set up an account? PLUS tips and hacks for advanced users
- Uniswap review and tutorial: Beginners guide and advanced tips and tricks
- Serum DEX guide and review
- SushiSwap ($SUSHI) explained
- 1inch Exchange, Mooniswap and Chi GasToken: The ultimate review and guide
More videos and articles are coming soon as part of our DeFi series, so be sure to SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel so you can be notified as soon as they come out!
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.