As savvy investors, it is easy to get carried away by flashy numbers like 1000% staking rewards. But what most beginners overlook is the three little letters standing right next to it: APY or APR.
Although APY and APR may sound identical, there is a significant difference to the calculations for returns over a period of time. There are also underlying risk factors of certain decentralized finance (DeFi) products with very high return on investment (ROI).
Therefore, it is crucial that you have a better understanding of the formulas used to generate these two measures as well as what they signify for the potential returns on your crypto investments.
What is APR?
APR, which stands for annual percentage rate, is interest you gain from your investment in a year. It is also known as “simple interest” and its formula is straightforward.
For example, if you stake 10,000 USDT at an APR of 10%, you will earn $1,000 in interest after a year. Your interest is simply calculated by multiplying the principal amount ($10,000) and the APR (10%). In a year, your capital will amount to $11,000, and in two years, it will be $12,000, and so on.
See also: The Pros and Cons of Stablecoins: Why You Need To Know How They Work
As such, APR is always quoted as a fixed yearly rate, thus a simpler and more static metric. However, with APY, interest calculations become slightly more complicated with compounding taken into account.
What is APY?
APY, short for annual percentage yield, is the annual rate of compound return earned on an investment. The keyword here is “compound.”
What is Compound Interest?
Compound interest is not only earning interest on your initial investment, but you are also earning interest on the accrued interests. This effect is called “compounding.”
A simple scenario would be like this. Let’s say this time you stake 10,000 USDT at an APY of 10% compounded monthly. This means that interest is added to your principal sum each month, and the sum on which you earn interest increases over time. In other words, you will have more money earning interest each month.
In one year, your capital will amount to $11,047.13, which is $47.13 more in interest by adding the effect of compound interest.
The Power of Compound Interest
The aforementioned scenario is an instance of monthly compounding. In fact, there are different compounding periods depending on the institution. Interests can be compounded quarterly, monthly, week, or daily.
The more frequent the compounding periods, the higher your effective yield is going to be. For example, if your staked 10,000 USDT is compounded daily at 10% APY, then you will earn $11,051.56 in one year, which is $4.43 more than monthly compounding.
It may not seem like a big difference but the power of compounding is more significant over more extended periods. After five years, you will have earned around $16,500 if compounded, which is $1,500 more than simple interest.
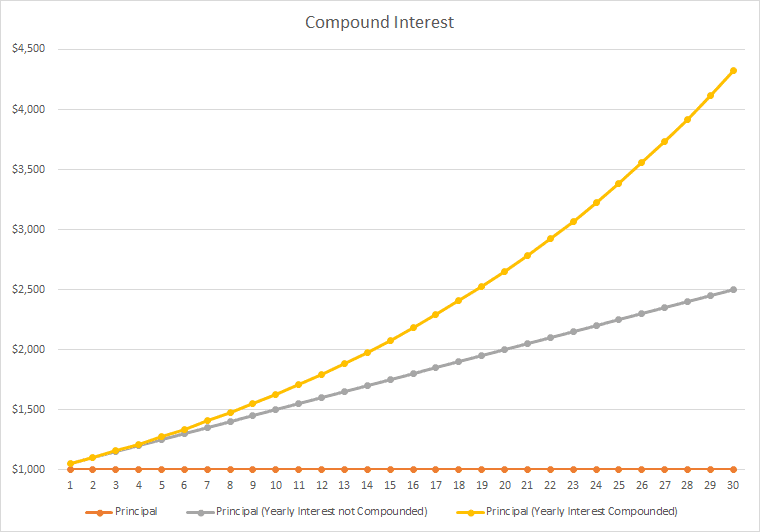
As illustrated in the graph above, the APR line is linear, whereas the APY line is exponential, which is always higher than the linear as time progresses. The principal remains the same if no investment is made.
You can use an APY calculator to calculate how much you can earn with different compounding periods and different time frames.
How does APY Work in DeFi?
The previous section is a simplified example of how compound interest works in general. However, APY investments work differently in DeFi. APYs in the crypto space constantly change due to several factors. As such, as a rule of thumb, the APY shown on DeFi products should be considered as estimates.
Supply and Demand
As with any market economy, the law of supply and demand influences the assets’ price. Since interest is generated based on the demand to borrow and trade crypto, market dynamics play a role in determining the rates.
Since the crypto market is volatile in nature, the APY changes according to the level of demand for trading liquidity of the token. If there is plenty of supply, APY interest rates tend to be lower. Conversely, if the demand is high, the APY usually increases as well.
Inflation
Inflation refers to the loss in value of a currency over time. In crypto, inflation is brought about by adding new tokens at a predetermined rate to the blockchain. The rate of inflation affects the staking returns. If the inflation rate exceeds the interest earned on a staked token, then the investor is losing money.
Different Compounding Periods
Different projects have specified blockchain protocols which play a part in the calculation of the APY. As a result, compounding periods may vary for each project. For example, some projects compound interest weekly, daily, or even according to the mined block per block cycle. It is important to note that the more frequent the compounding periods, the higher the APY will be.
Most crypto projects offer shorter compounding periods, with weekly compounding being one of the most popular ones. This is to help potential investors mitigate the effects of price swings in the long run, since crypto prices rise and fall over time. This way investors can do their compounding manually, and calculate their returns within specific time frames, so that they can strategize their entries and exits when engaging in DeFi protocols.
Comparing APY vs APR Investments
Although APY seems to be the obvious choice in maximizing ROI, there are also underlying risk factors when it comes to APY investments in general.
Prevalence of Non-Sustainable APY Projects
Projects with very high APYs, as high as 1,000% or more, are high risk/high reward investments. This is especially common for newly launched DeFi projects, because the price of a token is highly volatile during its early phase. To keep investors in the ecosystem, the project would provide trading pairs for the token also known as liquidity pools.
Liquidity pools are one of the products that allow for staking and generating returns for providing liquidity. As such, projects will offer high APYs to offset impermanent loss, which occurs when the ratio of tokens in the liquidity pool is unbalanced. This also incentivizes users to continue providing liquidity instead of selling.
However, there is a possibility of a dump for the project. Since most DeFi protocol tokens are inflationary in nature, the revenue capacity for the protocol might be insufficient for everyone to share. In other words, if everyone is earning 1,000% APY and the token has no real utility, it then becomes a race for the liquidity providers to see who cashes out first. As a result, this drives the token price and APY down, leaving real users of the protocol with no exit liquidity.
Distinction of DeFi Product Yields
Products with a higher APY will not necessarily generate more returns than those with a lower APR. It depends on what the APY and APR mean in relation to the DeFi product.
Some products advertise the term “APY” referring to the cryptocurrency earned, and not the actual yield in fiat currency. Some beginners often mistake the APY crypto rewards for fiat currency, which blindly clouds their judgement.
This is a critical distinction to point out because the value of your investment in fiat terms may increase or decrease depending on the volatility of crypto asset prices. Even if you continue to earn high APY in crypto, the value of your investment in fiat terms may still be lower than the initial amount you placed in fiat, should the price of the crypto asset decline.
Key Takeaway
APR (annual percentage rate) is interest you gain from your investment in a year. On the other hand, APY (annual percentage yield) is the annual rate of compound return earned on an investment, which means you earn interest on previous interests accrued.
Although APY is the obvious choice in maximizing ROI, there are also underlying risk factors behind it. Therefore, it is crucial to comprehend how these two measures are determined as well as what it means for the potential returns on your digital investments.