Over the past two years, Solana has risen to be one of the largest blockchains by both market cap and usage, rivalling that of Ethereum. This rapid growth was largely driven by Sam Bankman-Fried (SBF), former CEO of recently bankrupt exchange FTX, who was a huge proponent of the project. In light of the FTX contagion, Solana was hit hard, leaving investors to question the state of the ecosystem.
In case you are out of the loop, we have covered the entire timeline of the FTX contagion in chronological order listed down below:
- SBF vs CZ War: What’s happening with FTX and Binance?
- Binance to Acquire FTX: What This Means for All Investors
- Binance Will NOT Acquire FTX: What is Next?
- BlockFi suspends withdrawals over unclear status of FTX
- FTX, FTX US and Alameda File for Bankruptcy
- FTX Hacked: Hacker Identity Revealed by Kraken
- What will happen to BlockFi?
- Were BlockFi’s assets held on FTX?
How is Solana Affected by the FTX Collapse?
Solana (SOL) Token Holdings of FTX
According to an FTX balance sheet shared with investors, the exchange held $982 million in SOL. It is also reported by CoinDesk that the second largest holding of Alameda Research, the sister company of FTX, is SOL. It stands to reason that FTX and Alameda might have dumped their holdings to raise liquidity, though not confirmed.
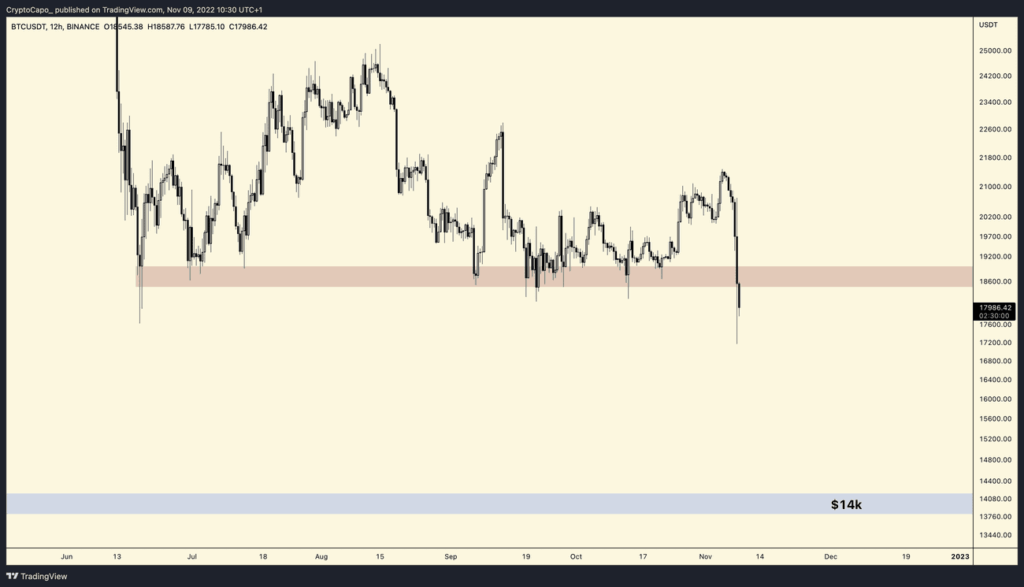
Since the beginning of FTX’s downfall, SOL has tanked -59% in price, putting it at -94% below its all-time high. It is also expected that many investors have exited their SOL position out of fear.
Moreover, FTX and Alameda Research purchased 50.52 million SOL tokens from Solana Foundation and 7.56 million SOL from Solana Labs, representing nearly 11% of the total supply. On the bright side, most of these tokens are vested through a linear monthly unlock mechanism, which means FTX do not have them in custody yet. The last of these unlocks will occur by January 2028.
Given FTX and Alameda are undergoing bankruptcy, their tokens will be frozen once unlocked, preventing further sell pressure. But it is likely that proceedings will involve liquidating SOL to repay FTX creditors.
Massive TVL Decline in Solana’s DeFi Ecosystem
Apart from SOL’s price, Solana’s DeFi ecosystem has also been severely impacted. Since the beginning of FTX’s downfall, more than $700 million have exited Solana’s ecosystem, leaving just a mere $285 million in total value locked (TVL) at the time of writing, according to DeFi Llama.
A lot of this has to do with Project Serum, an order book based decentralized exchange (DEX) laying at the heart of Solana’s entire DeFi ecosystem, providing liquidity and pricing data to many other major DeFi protocols. Unfortunately, Serum was launched by SBF, and most of its liquidity comes from FTX and Alameda. Moreover, the recent FTX hack revealed that the private key of Serum’s program was compromised, suggesting FTX insiders were in control of them. As a result, Serum developers forked the program to separate from FTX and protect end-users.
Depegged Wrapped Tokens on Solana
Another critical issue is that wrapped tokens notably soBTC and soETH are depegged. This is because these wrapped assets are backed by collateral held in FTX, but because their liquidity dried up, no one knows if FTX still has the underlying assets. As a result, these wrapped tokens are no longer redeemable.
This is very problematic, because almost all DeFi protocols have soBTC and soETH as collateral since it is accepted as the de facto BTC and ETH in Solana. But if underlying assets are completely invalid, then these wrapped tokens have no value, which could worsen the contagion.
Will Solana Make a Comeback?
It is important to remember that this collapse is from centralized players and not from decentralized protocols. The technology behind the Solana blockchain is not affected. Though Solana is experiencing big price declines, its community remains resilient and bullish as they continue to build despite market sentiment.
Better Technology for Solana
Recently, Coinbase Cloud has been helping with the network upgrade of Solana, implementing (1) Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC), (2) Stake-weighted Quality-of-Service (QoS), and (3) local fee markets.
- QUIC gives validators more control over incoming traffic. It will help prevent spammed transactions from overwhelming validators like in the April 2022 outage.
- Stake-weighted QoS ensures that validators can forwards transactions to slot leaders based on stake-weight, regardless of network conditions. Even if the slot leader is being spammed, other validators should be able to forward transactions to them. This QoS feature has been rolled out with QUIC.
- Local fee markets allow users to have their transactions included over others by adding a prioritization fee. This addition unlocks a new dimension in competing for transaction inclusion, whereas in the past, spamming was the only way to compete.
Moreover, Google Cloud is running a block-producing validator on Solana, introducing Blockchain Node Engine to the blockchain next year. All of these features together will immensely increase the throughput capacity of the network.
Improved Network Performance and Decentralization
As a result of recent development, network performance has improved as average time to produce a block has decreased, increasing transactions per second. Moreover, active user number on Solana remains strong despite this year’s market downturn. As of October 2022, there are 11.5 million active accounts and 1.7 million active fee payers.
Solana’s validator network is becoming more decentralized, ranking third on the Nakamoto Coefficient, a measurement for network decentralization. Furthermore, with FTX and Alameda expected to liquidate their SOL holdings, new buyers will come and help spread out the holding percentages, further increasing decentralization.
Strong Developer Community
In 2022, Solana has seen unprecedented developer activity across DeFi, DAOs, NFTs, GameFi, payments and mobile apps. Open source repos and developer activity on Solana surged this month, thanks to growing developer education resources and an easier onboarding experience. Additionally, DAO tooling and adoption has made it possible for large numbers of Solana projects to be managed on-chain.
Solana also has a thriving NFT ecosystem. Even after the dip, it remains the second largest NFT ecosystem, according to CryptoSlam!. Solana NFTs are onboarding hundreds of thousands of users to the network, with over $3.6 billion in primary and secondary sales.
According to sec3, a security research firm for Solana projects, thousands of developers are using, deploying, and auditing 1,000+ unique programs on Solana. Between the Phantom wallet, the NFT ecosystem, big partnerships with Instagram, and new use cases like StepN (move-to-earn), Solana continues to bring new users into the web3 space.
Final Takeaway
It is important to remember that Solana is NOT FTX. Even though Solana was heavily invested by FTX, its technology and decentralized protocol were never affected. The huge price declines we are currently seeing is most likely due to mass panic sells and forced liquidations of the FTX Group as well other ventures. As long as Solana continues to build, fresh healthy money will come flowing in the ecosystem.