What is The Graph?
The Graph ($GRT) is a decentralized and open-sourced indexing protocol for blockchain data. Developers can build and publish different APIs, which are referred to as subgraphs, and perform queries through the GraphQL.
The platform can easily be used to look for any Ethereum data conveniently through simple queries. This addresses the common problem faced by a lot of other blockchain indexing platforms.
Blockchain applications face difficulties in keeping properties like finality, chain reorganization, and security in their process of fulfilling query tasks. These are also potential complications that applications usually address, but unfortunately make the process of querying time-consuming. The Graph has a workaround for this, and it is built exactly for that purpose.
Through “subgraphs,” The Graph indexes blockchain data, which users can access via the GraphQL API. According to the team, they will make it fully decentralized in the future, where more nodes will be involved and made responsible for maintaining the index.
The interest for the platform is steadily growing. In fact, they hit over a billion queries last June 2020. This was right at the time when decentralized finance was also gaining much institutional attention.
Background
Yaniv Tal, co-founder and CEO of The Graph, together with his team, has created an indexing protocol meant to ease the process of accessing blockchain data. Tal and his co-founders had personally witnessed themselves how difficult it was to actually create new applications on the Ethereum blockchain.
Thanks to their experience on applications, they have found out that there is actually no decentralized indexing and querying softwares yet for blockchain. The problem back then was that developers had to come up with their own method to gather data and transform them from different sources.
The mission of the platform, which Tal and his team developed, is to help create applications that require no servers and make Web3 accessible to everyone.
How Does The Graph Index Data?
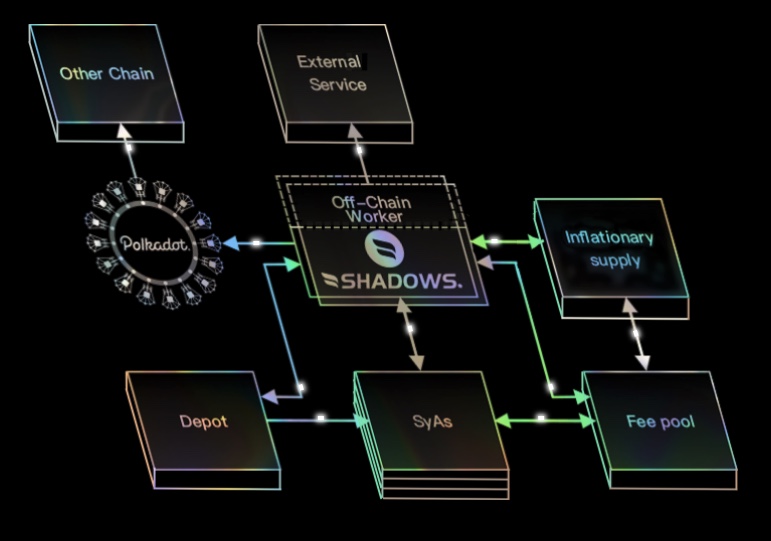
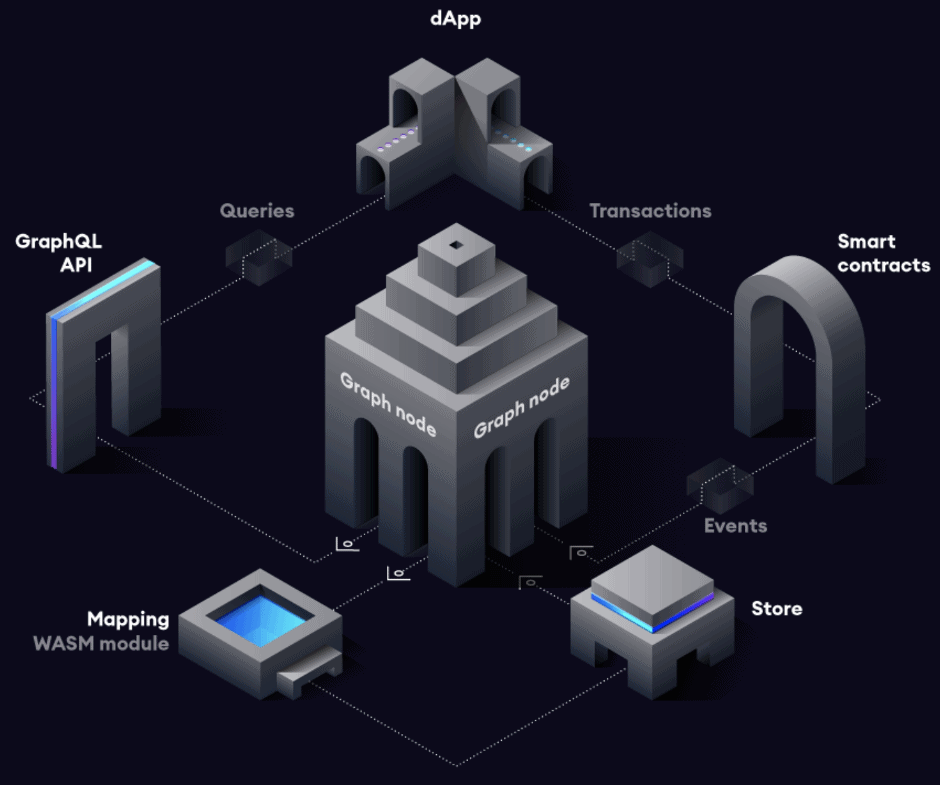
To index Ethereum-based data, The Graph uses the “subgraph manifest.” This refers to the description of a subgraph containing data about smart contracts, blockchain events, and the procedure in mapping event data with one another, before they are all kept in the platform’s database.
The flow of the data from transactions, subgraph manifests, and the database follows a particular structure. All of it begins with decentralized applications that are adding data to the Ethereum blockchain through the help of smart contracts.
All of that data will contain a record of all events and transactions up until the point that they have achieved finality. Then comes the Graph Node, which scans the whole blockchain database, gathers new data, and filters out those that are relevant to the queries that users make. To make the indexing much easier, it identifies every information that answers the questions from subgraphs.
GraphQL is the link between blockchain data and the application that a user wants to provide it with. But then again, it is through the Graph Node that users can deliver searches to the platform. After the whole process, users can finally look at the results of their query from their applications.
Basically, this is how the cycle of data query and indexing works in the platform. Users can refer to the Graph Explorer to scan through the subgraphs that are already in the platform. Each of these subgraphs have a playground where users can perform queries through GraphQL.
As of latest, The Graph can support the indexing of data coming from Ethereum, IPFS, and PoA networks. There are more networks that the platform will support in the future. But right now, they already have more than 2,300 subgraphs deployed, which developers for applications utilize. Some of these applications are AAVE, Aragon, Balancer, DAOstack, Uniswap, Synthetix, and many others.
There is a lot of institutional support for The Graph network. Michael Anderson of Framework Ventures, said in a press release that they “couldn’t be happier to back Yaniv and the team, and we look forward to helping grow the decentralized network when it launches.”
Hayden Adams of Uniswap also shared how useful the platform was for their analytics needs: “As a company we don’t manage or run our own databases. … Right now it’s pretty difficult to get historic data from the Ethereum blockchain in an efficient way.”
Their plan, apart from expanding to other blockchains soon, is to make it community-owned and governed in the future. This is also in response to the shift of many blockchain applications to a decentralized model of governance.
Key Roles
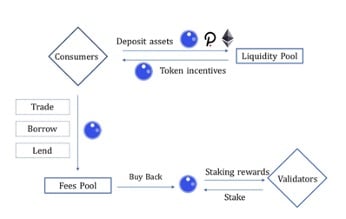
The platform’s whole ecosystem is composed of the following:
- Consumers – These are the users who pay indexers for their searches. It could also be web services or any other software linked with The Graph.
- Indexers – These are the nodes that maintain the indexing function of the platform.
- Curators – Using GRTs, curators identify to the subgraphs the information that is valuable for the platform’s index.
- Delegators – These are other stakers who delegate their GRT to existing indexers and earn a portion of the rewards run by nodes.
- Fishermen – They check whether the network’s response to queries is accurate.
- Arbitrators – They decide whether an Indexer is malicious or not.
The Graph Council
The Graph plans to decentralize its governance in the future. This will most likely be similar with MakerDAO and Compound. At the point of the protocol’s maturity, the team plans to launch a Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO) that would allow core interest groups to participate in important protocol decisions.
Similar to other DAOs, the Graph Council, which will be the governing body for the technical parameters of the protocol, is also in charge of how The Graph Foundation allocates its native, utility tokens.
Among their basic functions include decisions on allocating grants and ecosystem funding, protocol upgrades, protocol parameters, and other emergency decisions.
GRT Token ($GRT)
The Graph Token, or $GRT, is its native ERC-20 based token, which can serve as a medium of exchange and the reward distributed to community participants who function as Indexers, Curators, and Delegators.
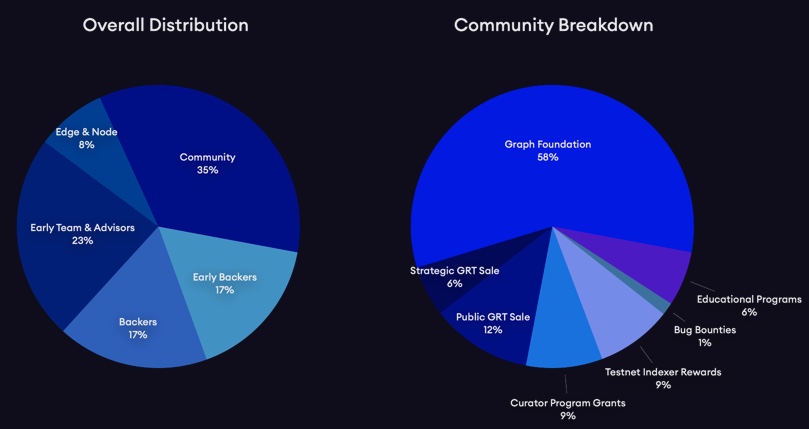
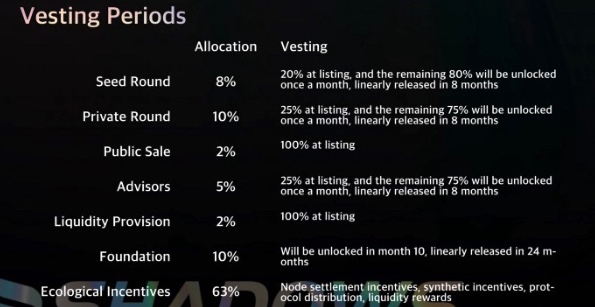
GRT also has a vesting and distribution schedule ranging between 6 months to 10 years depending on the bucket. Around 12.5% of the total token supply (i.e. 1,224,999,438 GRT) is expected to be in circulation at launch. However this figure is exclusive of stakeable but locked tokens.
GRT token distribution at mainnet launch
The Graph launched its mainnet at 9:00a.m. (PT) on 17th December 2020. Upon launch, GRT has been distributed to all of the participants of the public sale. Members of The Graph’s Curator Program also received an initial USD $1,000 worth in rewards, with the remainder to be distributed to them on a quarterly basis based on their contributions to the Program.
The Graph Foundation also received around 20% of the supply for the future development of The Graph. In particular, contributors who want to help building on The Graph can apply to their Grants Program, around 1% of the total supply of GRT will be allocated to support these participants in 2021.
Here’s a graph showing the GRT circulation over the course of 5 years from the date of launch (i.e. 17th December 2020 at 9:00a.m. PT)
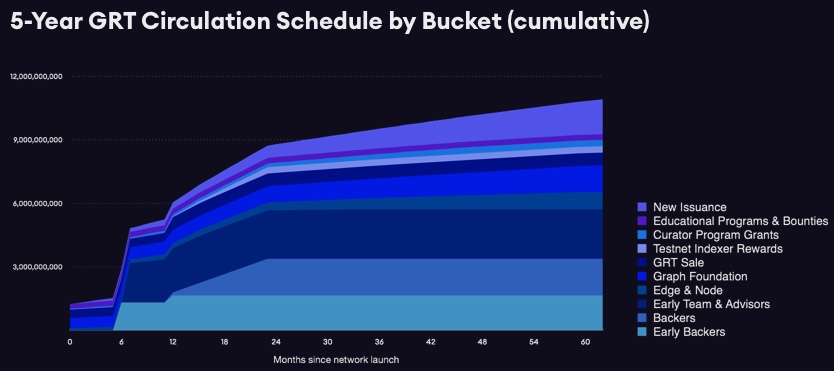
Indexers that assisted during the Testnet phase have also ben rewarded between USD$10,000 to USD$100,000 in GRT as a reward for their contributions.
In addition, around 2% of the total GRT has been granted to several Education Programs and loans totalling around 2.5% had been made to independent ecosystem partners.
Indexer Staking
In order for users to stake in the nodes that operate the whole platform and sell their services in the query market, they have to lock their GRT. In return, they are given financial rewards. If the indexers work maliciously, like altering data intentionally, the GRT that they staked will be slashed.
Mainnet now live!
The Graph Network launched its main net on 17th December 2020 after 3 years of development! According to the team the mainnet launch includes the following components: Deployment of The Graph Network contracts on Ethereum mainnet, deployment of the GRT contract, distribution of GRT to takeovers, launch of the Bug County Program and new docs for network roles.
With the mainnet launch, Indexers will first stress test and improve performance before supporting real query volume, which will be upwards of 5,000 queries per second. Of course, there will be rewards for Indexers who will now begin earning on-chain indexing rewards and query fees.
Graph Roadmap: What’s next?
Now that mainnet has launched, The Graph will continue building. The Team has stated that the Graph Foundation will work on building a production-ready Graph Explorer dApp and Gateway that will support all network contributors.
The Graph is also open to any individuals or third-parties that want to build for the network and as mentioned previously, they an apply to the Grants Program or collaborate with other community contributors.
Conclusion
Looking at the current boom of the DeFi space, we can see how important it is for developers to be able to freely access blockchain data. Making the process faster and less difficult for everyone could potentially influence the growth of the space as well as its reliability, security, and capacity.
Everyone saw the need to create a bridge of information between applications and blockchain data. The Graph sought out to answer that.
And with the deployment of smart contracts that depend on user data, The Graph has proven itself to be easy to use, cost-efficient, and fast. The platform is seen as a promising tool to empower everyone in the community, especially those who are developing more use cases for the blockchain.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
With content for both beginners and more advanced users, check out our YouTube DeFi series containing tutorials on the ESSENTIAL TOOLS you need for trading in the DeFi space e.g. MetaMask and Uniswap. As well as a deep dive into popular DeFi topics such as decentralized exchanges, borrowing-lending platforms and NFT marketplaces
The DeFi series on this website also covers topics not explored on YouTube. For an introduction on what is DeFi, check out Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Overview: A guide to the HOTTEST trend in cryptocurrency
Tutorials and guides for the ESSENTIAL DEFI TOOLS:
- MetaMask Guide: How to set up an account? PLUS tips and hacks for advanced users
- Uniswap review and tutorial: Beginners guide and advanced tips and tricks
- Serum DEX guide and review
- SushiSwap ($SUSHI) explained
- 1inch Exchange, Mooniswap and Chi GasToken: The ultimate review and guide
More videos and articles are coming soon as part of our DeFi series, so be sure to SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel so you can be notified as soon as they come out!
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.