Synthetix (SNX) is one of the top Decentralised Finance (DeFi) platforms in existence. According to Coinmarketcap their native token $SNX ranks no.7 in terms of market capitalisation compared to other DeFi tokens. Synthetix itself is primarily a decentralized exchange but also a synthetic asset issuance platform.
The platform enables users to issue and trade synthetic assets — digital assets that represent other real assets like stocks, fiat currencies, commodities, or cryptocurrencies. It also has a staking mechanism that incentivizes users to provide liquidity and maintain the platform.
The Synthetix Protocol was originally conceived as Havven back in 2017 by Kain Warwick. Warwick is currently also a Non-Executive Director of blueshyft- a network of over 1200 retail locations around Australia.
What is Synthetix?
Simply put, Synthetix is an Ethereum-based DeFi ecosystem that functions as a deentralised exchange (DEX) and asset issuer that is maintained via a staking incentive scheme.
Users can speculate on any real-world asset by creating synthetic assets that track their prices in real-time via oracle feeds. And unlike traditional financial systems, Synthetix requires no KYC. You don’t even need to create an account.
Yet anyone could gain exposure to Tesla stocks, high premium bonds, real estate, and just about anything. This can be done simply by depositing SNX tokens into the platform.
Furthermore, those that mint synthetic assets can earn passive income from the fees generated by people buying the assets.
One of the most exciting aspects of the Syntethix system is that it can siphon a huge chunk of the trillions of dollars of assets from traditional markets and bring them to the Ethereum network.
Synthetix Network (SNX) Token
SNX is the utility token of the Synthetix ecosystem and is necessary to create synthetic assets called Synths. Users can buy SNX tokens from several crypto exchanges and deposit them in a compatible wallet in order to stake them.
Once they are locked up, new Synths can be minted. The token’s supply used to be deflationary until it was updated in March 2019. The update saw the implementation of an inflationary monetary policy to encourage stakers to create more Synths.
By 2025, a total of 250 million SNX tokens will be minted. SNX has surged drastically in the last couple of months. It went from $0.79 at the beginning of June to around $3.32 on the 25th of July 2020.
Synth Tokens
Synth tokens are synthetic assets that track the price of real assets. They are minted by locking up SNX tokens.
Synths can come in any form and they are denoted by ‘s’. For instance, fiat synths would look like these: sEUR, sUSD, SRMB. Other variations of Synths include sAAPL (synthetic Apple), sTSLA (synthetic Tesla), sAu (synthetic gold), sBNB (synthetic Binance Coin), sDEFI (synthetic DeFi Index), and many more. (https://www.furtenbachadventures.com/)
Whenever new Synths are minted, stakers create a debt. Therefore, they need to pay back the same value in Synths before they can withdraw their locked-up SNX tokens. And the value of Synth will likely change over time.
As a result, users may need to pay a different amount of Synths by the time they withdraw their locked up tokens.
Fortunately, users are not required to pay the same type of Synth that was initially minted. As long as the Synth used to pay has the same market value, the system will accept it. For instance, a Tesla share Synth can be used to pay in the place of a Bitcoin Synth as long as they have equal value.
One thing to note is that Synth tokens are not exactly the same as the assets they represent. They are known as synthetic assets for a reason.
For instance, if you hold an sAAPL token, you will be exposed to the volatility of Apple shares. However, unlike owning real AAPL shares, you won’t be receiving dividends like real Apple shareholders enjoy.
Collateralization
The Synthetix system requires a collateralization rate of 750%. For instance, if you want to mint 100 sUSDT, you need to deposit $750 worth of SNX tokens as collateral.
This rather high collateralization rate is imposed in order to hedge the platform against extreme market price swings.
Staking SNX
Staking is currently where most people are making money out of the Synthetix protocol. But like any money-making schemes, staking Synthetix bears some degree of risk.
How to stake SNX
If you truly want to make money staking SNX, there are a few easy steps involved.
- First, you need to buy Synthetix in any exchange and connect to a web3 wallet.
- Visit Mintr, the best portal interface for minting and managing Synths.
- Connect your web3 wallet to Mintr.
- Click ‘Mint’ and choose what type of Synth you want to mint.
- Remember the collateralization ratio of 750%
- Input the number of Synths you want to mint.
- Click ‘Mint Now’.
- Confirm the transaction in your web3 wallet.
Afterward, your SNX token will automatically be staked. You will now be able to enjoy rewards generated from trading fees. Furthermore, you are also subject to inflation rewards.
These rewards, however, come with a price. When you mint Synths, you get to own a portion of the platform’s debt pool — the total value of all Synths. And this debt can increase and decrease regardless of the original value of your minted Synths.
Synthetic DEX
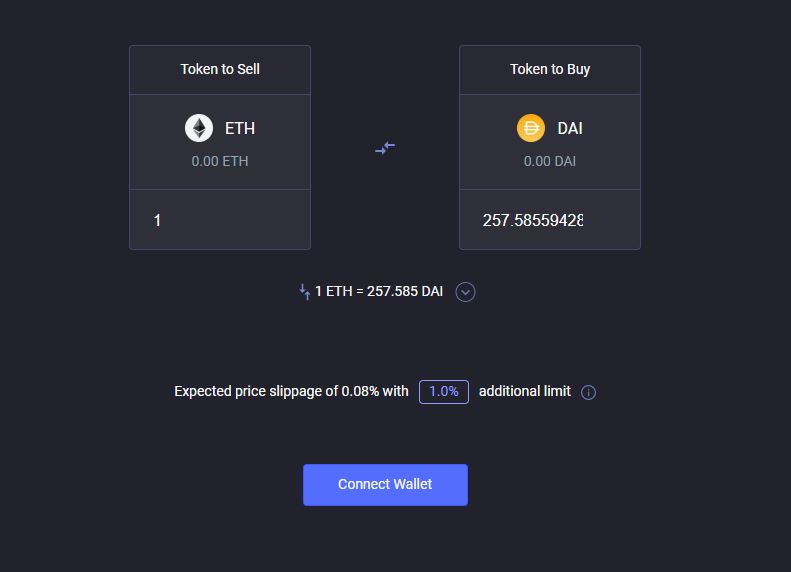
Synthetix has a built-in DEX interface that enables users to trade without an account. The DEX currently offers 19 assets to trade and 31 trading pairs.
All you need to do is visit the Synthetix exchange and connect any web3 wallet like MetaMask. It has a slick but simple interface that eases users’ experience while trading.
Synthetic exchange charges both maker and taker fees with 0.30% which is higher than the industry standard of 0.05-0.25%. The fees will be used to reward the stakers for providing liquidity to the platform.
Furthermore, users will also be charged Gas fees by the Ethereum network. For now, all these fees could add up which might be a hindrance from the greater market to fully adopt DEXes for all their trading needs.
In time, when Ethereum finally scales, gas fees should be low enough to become negligible.
DEXes like Synthetix don’t require withdrawal fees (except for Gas) since trades are conducted directly from wallet to wallet.
The Takeaway
As a leading DeFi protocol, Synthetix has a lot of potential. It has enabled users across the world to create and trade synthetic assets more than any platform to date. However, nothing is guaranteed to last in the crypto space.
DeFi protocols like Synthetix have seen enormous growth in the last couple of months. Whether or not this is sustainable, only time will tell.
But considering the trillions of dollars floating in Centralized Finance (CeFi), it is not far-fetched to assume that DeFi’s disruption is far from over.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
With content for both beginners and more advanced users, check out our YouTube DeFi series containing tutorials on the ESSENTIAL TOOLS you need for trading in the DeFi space e.g. MetaMask and Uniswap. As well as a deep dive into popular DeFi topics such as decentralized exchanges, borrowing-lending platforms and NFT marketplaces
The DeFi series on this website also covers topics not explored on YouTube. For an introduction on what is DeFi, check out Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Overview: A guide to the HOTTEST trend in cryptocurrency
Tutorials and guides for the ESSENTIAL DEFI TOOLS:
- MetaMask Guide: How to set up an account? PLUS tips and hacks for advanced users
- Uniswap review and tutorial: Beginners guide and advanced tips and tricks
- Serum DEX guide and review
- SushiSwap ($SUSHI) explained
- 1inch Exchange, Mooniswap and Chi GasToken: The ultimate review and guide
More videos and articles are coming soon as part of our DeFi series, so be sure to SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel so you can be notified as soon as they come out!
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.