Crypto futures trading allows traders to have exposure to cryptocurrencies without the need to own the underlying crypto asset. Binance exchange offers futures trading to users through Binance Futures, which has 279 trading pairs. This article provides a guide on how to trade on Binance Futures.
Get 20% off fees when signing up for Binance with the following link!

What is Binance?
Binance was launched in 2017 and is arguably the world’s most popular centralized cryptocurrency exchange. It has over 2 billion average daily volume and 72 million site visits daily. The Binance ecosystem includes Binance exchange, BNB Chain, Trust Wallet, Binance card, and other services.
What is crypto futures trading?
Crypto futures contracts create an obligation for parties to exchange the asset at a predetermined price and date. On most cryptocurrency exchanges, however, the parties can settle for the cash equivalent. But, the trade must take place.
Traders use futures trading to profit from market movements by going either “long” or “short” on a futures contract. Going “long” means that a trader purchases a futures contract expecting it would increase in value in the future. And if the value of the cryptocurrency does increase, the long trader would profit. On the other hand, a trader going “short” means they are hoping prices will drop.
Learn more about crypto futures trading with our guide- Crypto Futures Trading: What is it?
What is Binance Futures?
Binance Futures allows users to trade crypto futures contracts on Binance. It has 279 trading pairs and has the second-highest 24-hour trading volume amongst all crypto derivative exchanges. Binance Futures offers USDⓈ-M Futures and COIN-M Futures. These are perpetual or quarterly contracts settled in USDT/BUSD, or cryptocurrency respectively.
Binance Futures also has interesting features such as a leaderboard, showing traders with the highest ROI or PNL. Other traders can follow these top traders and see what positions they are holding, as well as copy their trades.
For traders who are more competitive, Binance Futures has a battle mode where you can guess whether prices will rise or fall within the next 1 or 5 minutes. Then, you will be matched with another player who predicted in the opposite direction. Players will still gain points regardless of whether they win or lose. Points can then be used to earn further rewards.
Binance Futures trading fees
Binance uses a maker-taker fee structure. Maker trades are orders that go on the order book partially or fully e.g. limit orders. Taker trades are executed immediately before entering the order book. Market orders are a type of taker trade. The fee charged depends on which type of trade. As maker trades add volume to the order books and thus “make” the market, it is in an exchange’s interest to have more of these orders. Therefore, maker fees are usually lower than taker fees.
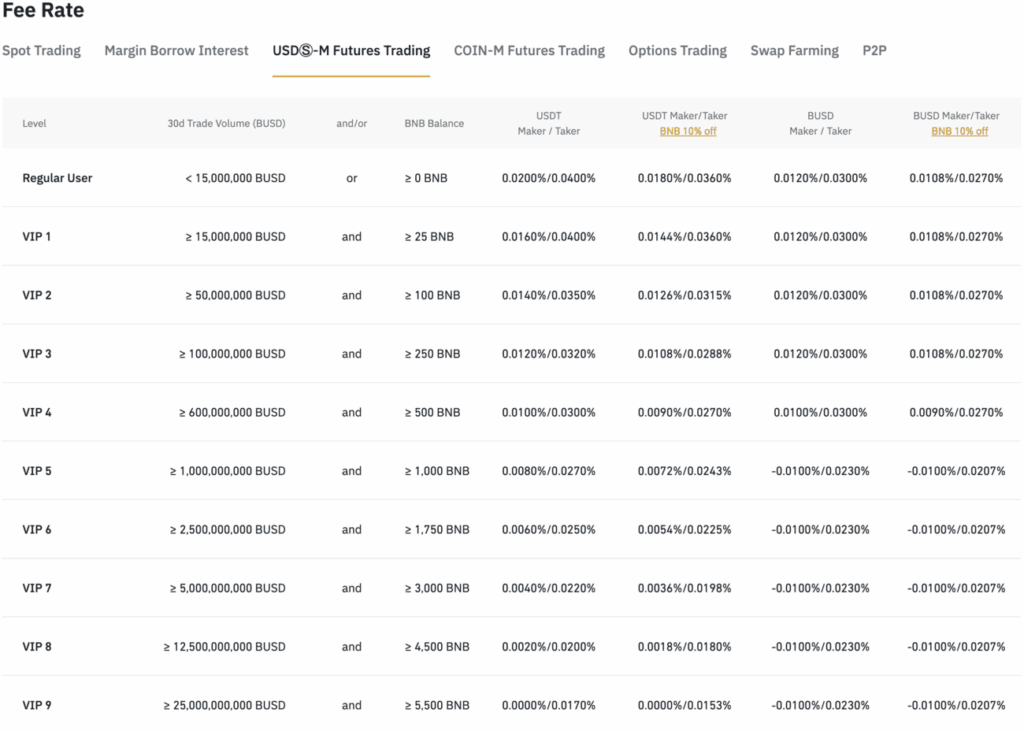
Binance also has a 9-tier VIP structure which offers progressively lower fees for users with high trade volume and substantial BNB holdings. Users who use BUSD, Binance’s USD stablecoin, or BNB for settling fees are also rewarded with lower trading fees.
The lowest tier, i.e. “Regular users” are traders with a past 30-day trading volume of less than 15 million BUSD or hold 0 BNB. For regular users, the maker/taker fee for USDⓈ-M futures trading is 0.02%/0.04%, and for COIN-M futures, the maker/taker fee is 0.01%/0.05%.
Highest tier users i.e. VIP 9, users must have a past 30-day trading volume of over 25 billion BUSD and hold over 5,500 BNB. VIP 9 users enjoy a maker/taker fee of 0.00%/0.017% for USDⓈ-M futures trading, and for COIN-M futures, the maker/taker fee is -0.009%/0.024%.
Extra discount! Enjoy 20% off fees when signing up for Binance with the following link!

Pros and advantages of trading on Binance Futures
Binance is one of the leading cryptocurrency exchanges. According to CoinGecko, Binance has the second-highest trading volume with over US$35 million being traded in 24 hours. Here are some of the pros and advantages of crypto trading on Binance Futures:
- Many trading pairs. Binance Futures have 279 trading pairs, giving traders a wide range of options from popular cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin ($BTC), to meme coins such as Shiba Inu ($SHIB).
- Low trading fees and generous fee structure. Maker/taker fees start at 0.02%/0.04%. However, Binance Coin ($BNB) and BUSD holders, and high-volume traders are entitled to discounts, bringing trading fees to as low as 0.0100%/0.0207%.
- Low minimum trade amount. Traders can start with a minimum trade amount of 0.001 BTC on the BTCUSDT Perpetual market.
- Binance offers up to 100x leverage. This allows more experienced traders to potentially maximise their gains.
- Binance has trading tools such as Grid Trading, TWAP, Advanced TP/SL, and Multi-Symbols Trading Page for maximum trading efficiency.
Cons and disadvantages of trading on Binance Futures
- Futures trading is not available in the US. So US traders will need to use other exchanges for futures trading.
- Users must pass the verification process in order to begin using Binance Futures.
Is Binance Futures trading safe?
Binance has a US$300 million Insurance Fund to protect traders. The Fund acts as a safety net to protect bankrupt traders from adverse losses whilst ensuring that winning traders are paid in full. The purpose of Binance’s insurance fund is to limit counterparty liquidations. Counterparty liquidations are where the positions of opposing traders are automatically liquidated in order to cover a bankrupt trader’s position. The insurance fund takes the remaining positions when a trader in liquidation has less than 0 USDT after all their positions are liquidated. These remaining positions would be offloaded onto the market gradually and liquidation fees will be collected from users that do not result in bankruptcy.
Binance also has a Cooling-Off Period function to help traders prevent compulsive trading behaviours. It works by preventing traders from trading futures-related products on the exchange for a predetermined period.
How to start trading on Binance Futures
Trading on Binance Futures only requires 5 simple steps.
1. Sign up for a Binance Account
To sign up AND get an additional 20% off trading fees click here.
Alternatively, on the Binance main page, click register and enter your details. Don’t forget to fill in GQWT3T1T for the Referral ID in order to be eligible for 20% off trading fees.
You can sign up with your phone, email, Google, or Apple accounts.
2. Open a Binance Futures account
Go to Binance Futures and click Open Now, if prompted, you can enter GQWT3T1T as the Futures referral code in order to enjoy 20% off trades. Then, complete and get all the answers correct on the 14-question quiz on how to use Binance Futures.
3. Complete the verification process
Click Profile and then Verification. Follow the steps and fill in your personal information. A government-issued ID (e.g. a passport) and address proof must be provided, and you must also pass the facial recognition test.
4. Make a deposit into your Binance account
Binance allows you to deposit fiat or cryptocurrencies into your account. To deposit, click on your profile and go to Dashboard. Under Fund your Account, you can choose to Buy crypto using Mastercard, Visa, Google, or Apple Pay. Users can also choose to Deposit crypto from other exchanges or their hardware wallet.
5. Start trading
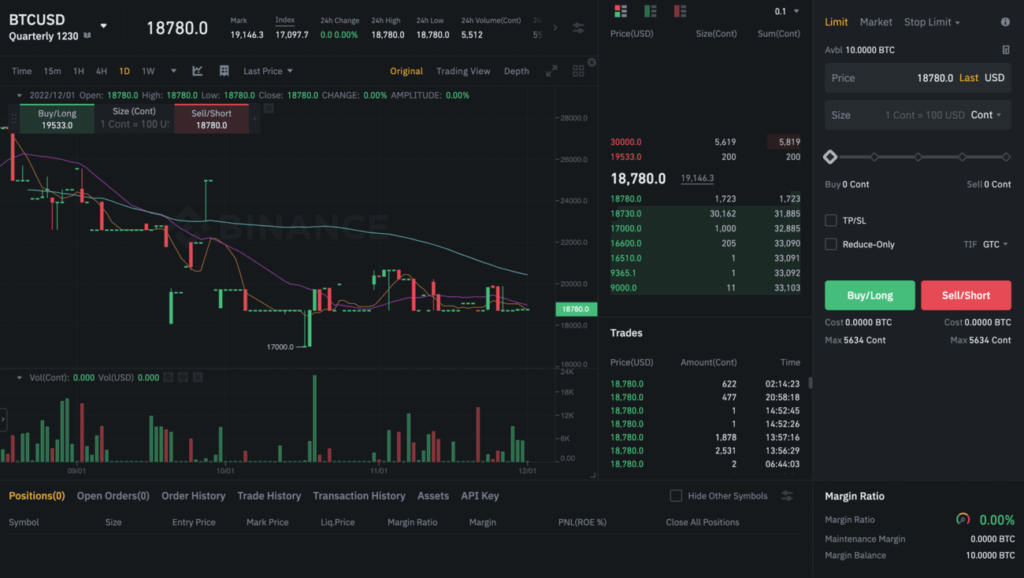
On Binance Futures, choose between USDⓈ-M and COIN-M Futures Contracts. On the top left-hand corner (marked in yellow), you can choose which futures contract to trade.
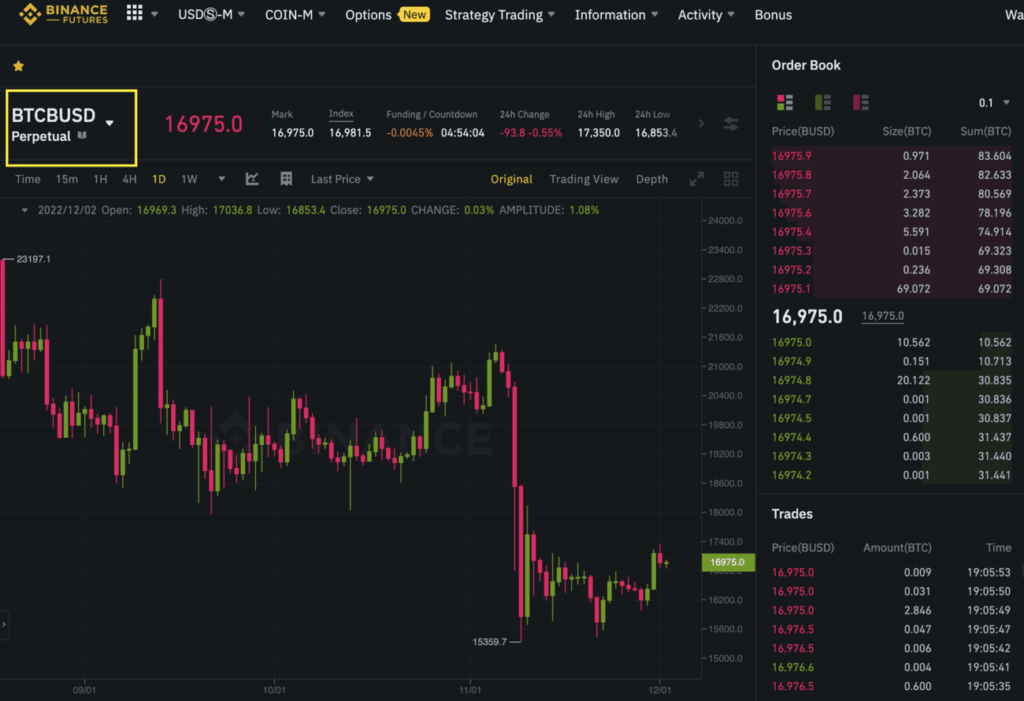
On the left-hand side, there are various tools to help you identify patterns or trades such as trend lines, arrows, or Fibonacci retracement. You can use these tools to annotate your charts.
On the top right-hand side of the page, you can select the Margin Mode. Users can choose between Cross or Isolated margin modes. Cross-margin mode means that the entire margin balance will be shared across open positions. However, if there is a liquidation event, the risk is that their entire margin balance and any open positions may be lost. Isolated margin mode, on the other hand, allows traders to manage their risk on individual positions by restricting the amount of margin allocation. The benefit of isolated margin mode is that if a position is close to being liquidated, users can allocate additional margin to that position.
Set your Leverage (if any) by clicking on the top right-hand corner. Traders can set the leverage from 1x to 125x. However, traders should be careful that setting high leverage could result in significant losses in the event of a liquidation.
On the right-hand side of the page, you can also select the type of order (e.g. Limit, Market, Stop Limit, etc), the order price, and size. For a more automated yet managed trading experience, traders can also select TP/SL i.e. when to take profits, or stop loss. Finally, traders need to select between a Buy/Long, or Sell/Short order.
Is Binance Futures safe?
Binance Futures comes with security features expected from every reputable cryptocurrency exchange. Binance Futures requires users to have passed the KYC verification before they can start trading. Before trades are executed, users must also have enabled 2FA authentication and will be sent an Anti-Phishing Code for verification.
Binance Futures also has a nearly US$300 million insurance fund to protect bankrupt traders from adverse losses. It also ensures that profits of winning traders are fully paid out.
Finally, if users really need help, Binance offers customer support in 17 different languages via Live Chat or email.
Conclusion
Trading futures contracts are a great way for cryptocurrency traders to profit from fluctuations in cryptocurrency prices. Furthermore, Binance Futures is a popular exchange for traders of any level to trade futures since they have a large number of trading pairs. Binance Futures also has the benefit of a huge insurance fund, helpful tutorials, and customer support to ensure that customers have a straightforward and secure trading experience.
Enjoy 20% off fees when signing up for Binance with the following link!