Ethernity Chain is a blockchain-based platform that deals with limited authenticated NFTs from top artists and with endorsements from popular figures in the sporting and entertainment scene.
Although Bitcoin concentrated on hedging away from government-issued currencies, its blockchain technology opened a much bigger world of possibilities. For example, Ethereum tapped into the technology to build a decentralized computer and power decentralized applications (Dapps). Next came decentralized finance (DeFi). Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) then followed suit.
However, most NFT projects concentrate on the broad digital artwork space. Consequently, they fail to address specific problems in any of the artwork subsections. This leaves room for platforms such as Ethernity Chain to take over. Below is a detailed overview of the platform and what it brings to the NFT ecosystem.
Background
Ethernity Chain is a community-focused project that banks on artworks from top artists and stars. The project’s team is led by Nick Rose Ntertsas, the platform’s founder and chief executive officer.
What is Ethernity Chain?
Ethernity Chain deals with limited authenticated NFTs from top artists and with endorsements from popular figures in the sporting and entertainment scene.
Its vision is to raise funds for charitable causes while at the same time keeping NFT creators motivated. The charity offerings ride on the project’s for-profit status that allows it to design services for more users compared to non-profit themed networks.
Apart from charity, Ethernity Chain provides a crucial connection between non-fungible tokens and the wider DeFi industry. Consequently, it enables increased access to rare and collectible virtual artworks designed by reputable artists and features respected public figures. Notably, featured celebrities must approve the NFTs using a digital signature, known as aNFTs.
What are aNFTs?
aNFTs are authenticated non-fungible tokens- a unique creation of Ethernity Chain. These aNFTs are authenticated by the creator so that purchasers or traders know it is officially endorsed by them.
Users can buy these aNFTs using Ethernity Chain’s native token, known as ERN. ERN can be purchased on the market or earned when users LP stake and earn ERN and use these rewards to purchase aNFTs.
Pelé charity aNFT collection
Ethernity Chain has recently released the officially licensed collection from renowned football legend Pelé. The collection will comprise authenticated non-fungible tokens (aNFTs), of which 3-6 pieces will drop on the Ethernity Chain platform on 2 May 2021.
90% of the proceeds from the sale will go towards the Pelé Foundation, a charity that empowers and educates children battling poverty around the world.
Major Ethereum Chain Products
Ethernity Packs
Here, NFTs have a community focus and employ a lottery model. Notably, these packs have a minimum and maximum price of $50 and $300, depending on rarity. The Ethernity Chain team curates all the collectibles in this category.
To awaken collectors’ taste buds, the team hides rare NFTs inside random packs, and collectors won’t know what’s inside before purchase. Also, the packs are available at different times on the network. Interacting with this product requires the platform’s native asset, ERN. Note that Ethernity Packs have a connection to STONES.
STONES
STONES is a product earned through staking the native token. In other words, it’s a farm-only offering. The farming process involves interfacing your MetaMask wallet with Ethernity Chain using the Ethernity.io platform.
Note that one ERN coin gives its holder 1000 STONES when locked in the farming contract for one day. Unfortunately, STONES are indivisible. As such, if you unlock your ERN tokens before the completion of the staking cycle, you end up with no rewards.
Additionally, STONES cannot be transferred from the farming contract, have no monetary bearing, and can’t be swapped with ERN or Ethereum (ETH). This leaves them exclusively for exchanging with a select number of NFTs on the protocol.
March 24, 2021, marks the first STONES farming spree, with the second slated for the end of April the same year.
Ethernity Chain ($ERN) Staking and Rewards
Ethernity Chain runs a staking program for liquidity providers. However, the rewards go to those who choose to interact with the ERN/ETH pair on Uniswap. Staking has a lockup period of 30 days, after which the pool is restarted. The annual percentage yield (APY) for staking fluctuates between 100 and 300% and has a monthly payment plan.
How the ERN staking process works
- First, deposit tokens in Uniswap’s V2 ERN/ETH pair.
- In return, the decentralized exchange (DEX) issues LP tokens equivalent to your stake in the pool.
- Next, access the staking option on Ethernity and connect your wallet address that holds the assigned LP tokens. Then, approve and lock the tokens into the staking contract known as the Liquidity Reward Program.
- Note that Ethernity Chain ties the unstaking event with claiming ERN. As such, unstaking automatically claims the native asset.
- Staking rewards are calculated by dividing the amount of LP tokens a staker has in the contract with the total amount of LP tokens padlocked in the staking contract.
Ethernity Chain ($ERN) Tokenomics
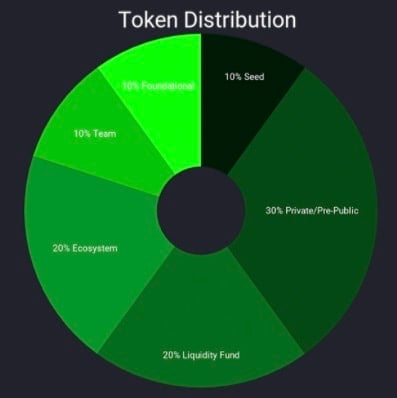
The total ERN supply is 30 million tokens. Token distribution includes to team/advisors (20%), partnerships (8%), expansion (6%), staking/rewards (12%), and reserves (15%). Also, there’s a 30.6% allocation to private price sale, 3.33% to a public initial digital offering (IDO), and 5% to liquidity.
However, some of the allocations have different freeze and unlock times. For example, the private sale has a two-month vesting period, while distribution to partnerships has 14 months vesting time.
Ethernity Chain Strategic Partnerships and Investments
Ethernity has its eyes set on interacting with the larger cryptocurrency industry. As such, it has inked notable partnerships with major firms building different products. For example, the protocol partnered with Kenetic, a reputable global blockchain-focused firm working to drive the adoption of decentralized protocols by offering investments, technology, tech, and advisory services. Kenetic’s managing partner, Jehan Chu, believes “NFTs are the true missing link between online and offline objects.”
They have also partnered with Chainlink by integrating Chainlink’s oracle solution to secure the minting and pricing of aNFTs.
Another notable partnership is with Terra Virtua, an inter-blockchain NFT protocol. Terra Virtua, through its Terra Virtua Kolect platform, provides a tailor-made marketplace for NFT collectors and creators on the web, mobile, and PC environments.
Conclusion
With a growing NFT ecosystem, Ethernity Chain provides a specific solution to the sector. For example, its focus on authenticated digital artworks gives collectors assurance of rarity, among other things.
Notably, the works are authenticated by globally renowned individuals such as Tony Hawk, a skateboarding legend, and Fernando Tatis Jr., a high-profile baseball player. Also, partnering with major firms like Terra Virtua and Kenetic boosts its vision in the future of the non-fungible industry. (https://www.smallhandsbigart.com/)
Also, other hidden gems inside Ethernity Chain Packs keep the collector’s hope alive. STONES add fun to the NFT farming while staking allows liquidity providers to earn rewards.
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.