Among the growing list of emerging decentralized exchanges lies THORChain and their RUNE token. The Company is one of many decentralized finance (DeFi) options in a field that is creating much buzz within the industry. The decentralised liquidity network, whose successful seed funding was completed last year, is one that should not be missed by those who are looking into this field. After a successful mainnet launch, the cross blockchain answer to Uniswap was made official in the first part of this year. As such we have compiled a complete guide to EVERYTHING you wanted to know about THORChain, answering questions like ‘What is THORchain?’, ‘Who Uses THORChain’ and other important topics.
What is THORChain?
First imagined in 2018, THORChain offers a wide range of services on its decentralized permissionless network. It allows for swapping of assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum as well as providing continuous liquidity pools for users. The platform uses a cross chain and can be used on any blockchain/with any asset, unlike other decentralized exchanges.
Their development paper outlines the core conception of THORChain, saying: “THORChain is a liquidity protocol designed to connect all blockchain assets in a marketplace of liquidity through cross-chain bridges and continuous liquidity pools secured by economically incentivised validators.”
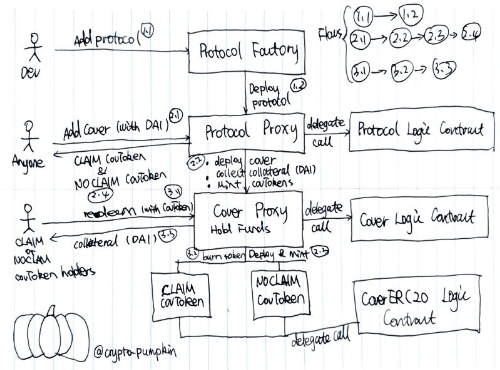
THORChain’s consensus is Proof-of-Stake and built on Tendermint, with network validators required to bond (lock up) their native token, $RUNE. Validators are punished for bad behaviour by having their stake slashed, which in turn disincentivises such actions.The network’s data is calculated and overseen using Midguard API service and is secured and bonded by ThornNode, which also powers the network. The nodes make vaults and validate the transactions on the site.
Who uses THORChain?
Users
These are the main participants and they usually use the cross chain services between the pools with them paying a slip fee. The fee is paid due to gas fees on external services and for fast execution. However, swapping is non custodial and unrestricted on different chains.
Liquidity providers
These are secondary participants who add liquidity to the various pools which is then bound with RUNE in a separate vault. Using the continuous liquidity pool means the network does not need oracles or have a price feed. Liquidity rewards are earned through fees generated from pools and are paid out when users withdraw. As the THORChain website explained, “liquidity is provided by stakers who earn fees on swaps, turning their unproductive assets into productive assets in a non-custodial manner. Market prices are maintained through the ratio of assets in pools which can be arbitraged by traders to restore correct market prices.”
Nodes explained
Nodes are the basis for THORChain’s services. They have three main functions, these are: to Bond RUNE, create vaults (which are like wallets) and witness transactions/produce blocks. They are all run by node administrators who are also rewarded for their work through bond rewards. For a full breakdown of node operators, please click here.
In terms of THORChain, as previously mentioned, nodes earn two-thirds of the System Income and they make vaults and validate the transactions on the site. Nodes are anonymous, with plausible deniability on all transactions. The nodes are created every three days and compete to enter with bonded capital. The oldest nodes are churned out and replaced when necessary. This allows the nodes to stay fresh and keeps the network constantly updating itself.
RUNE token: what is it?
Another integral part of the system and the nodes that run it is THORChain’s native token, RUNE. Available through Binance Chain, the token is a BEP2 token.The RUNE token is used in all liquidity pools and is bonded by nodes. All RUNE tokens are at a 1:1 ratio to asset value and this allows for pools to be linked. RUNE is also the rewards for pools, with the equivalent of 1/3rd of the System Income providing continuous liquidity incentives.
Alongside providing on chain liquidity, RUNE is also an important part of the THORChain security. This is because it protects against malicious actors by offering them a larger benefit for liquidating then they would receive from corrupting the system, as nodes earn 2/3rds of the System Income. Thus all transactions using RUNE on the system have double the amount at a 67% to 33% ratio. The other third is for liquidity providers. Not only that, but in terms of security nodes are also closed when malicious activity is detected.
RUNE has a total supply of 500 million tokens. Of which 100 million will be sold to the public in 3 stages, 150 million has already been allocated throughout the team, community and operational reserves, and the remaining 220 million is saved for the emissions reserve.
How to earn RUNE?
RuneVault: Liquidators and users of RUNE can have access to the RUNEVault feature which allows you to store and stake the token, with returns on investment. Using a Binance Chain Feature, users can “freeze” their tokens even if they have staked them meaning that the currency is always in the wallet. Earnings are based on weekly RUNE staked, but this weekly taking is reset should you withdraw any amount.
Rewards
THORChain offers rewards for all participants on the network. The rewards are paid out through the distribution of system income. This is worked out by Swap fees plus Block rewards. Swap fees are paid by users when swapping assets and Block rewards are worked out on an emission schedule. As mentioned previously, the system income is paid 67% to the nodes and 33% to the liquidator. However, this ratio is officially worked out by the incentive pendulum.
Governance on THORChain
THORChain attempts to have a minimal governance model. Instead staked capital is the main driver of the market and developers respond accordingly. New assets are easily listed and this means there are rarely many governmental decisions to undertake and it is truly decentralized in many ways.
Who is the team behind THORChain?
The team behind THORChain is purposefully pseudoanonymous. According to their website, “figureheads, personalities and founders undermine a project’s ability to decentralise,” and that, “transparency is demonstrated in other facets (treasury, code, research)”. That being said, there are 10 employees listed on LinkedIn and 12 team members listed with 6 additional advisors on ICOBench.
What sets THORChain apart? What are its benefits?
THORChain takes a little while to understand the basics and the nodes that run the network. However, once you get the hang of the exchange then THORChain has a number of benefits.
The main benefit is that with their cross chain feature, any asset can be swapped and a pool created around it. That gives users a huge amount of variety and does not hem them in unlike other decentralized exchange options do. This opens a whole new world of possibilities for DeFi users and one that should be applauded.
Conclusion
For those who are fans of Uniswap, then this decentralized option could be a great alternative. Yet, as Balancer has shown with their recent security scare, the often precarious nature of DeFi security does cause concern. Perhaps though, THORChain with their incentivized payments negates this risk. However, until more is known about the site and they are around for longer it will be hard to make a final judgement.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
With content for both beginners and more advanced users, check out our YouTube DeFi series containing tutorials on the ESSENTIAL TOOLS you need for trading in the DeFi space e.g. MetaMask and Uniswap. As well as a deep dive into popular DeFi topics such as decentralized exchanges, borrowing-lending platforms and NFT marketplaces
The DeFi series on this website also covers topics not explored on YouTube. For an introduction on what is DeFi, check out Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Overview: A guide to the HOTTEST trend in cryptocurrency
Tutorials and guides for the ESSENTIAL DEFI TOOLS:
- MetaMask Guide: How to set up an account? PLUS tips and hacks for advanced users
- Uniswap review and tutorial: Beginners guide and advanced tips and tricks
- Serum DEX guide and review
- SushiSwap ($SUSHI) explained
- 1inch Exchange, Mooniswap and Chi GasToken: The ultimate review and guide
More videos and articles are coming soon as part of our DeFi series, so be sure to SUBSCRIBE to our Youtube channel so you can be notified as soon as they come out!
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.