Week in review
Bitcoin makes front page news
On 24th August 2020, a full-page advertisement appeared on Hong Kong newspaper Apple Daily. The advertisement tells people “Banks, today you are not ditching me, I am ditching you” (in Cantonese) and “Bitcoin will never ditch you”. The advertisement does not promote a specific cryptocurrency-related business of service. Rather it only seems to educate readers on what is Bitcoin, saying: “Bitcoin is digital money. It is not issued or controlled by any government or corporation. Nobody can stop you from transacting on the network and it cannot be shut down. Bitcoin is available to anyone regardless of their nationality, gender, or beliefs. Bitcoin began with the GENESIS BLOCK during the financial crisis of 2009. Now, its time is coming.”
Apple Daily is one of Hong Kong’s largest print media, made even more popular recently due to their CEO’s arrest for alleged violations of Hong Kong’s National Security Law, though he has since been released from custody.

Cleaning house
Recently with the increased interest in cryptocurrencies, I have been frequently asked what are my main coins for 2020. With all the different projects I’ve been looking into I realised that I am holding so many coins such that it is becoming difficult to manage. So this week I’ve cleaned my portfolio a bit and identified my “medium bags”. These are coins which I believe have a proven use case and a reason to go up in value. These “medium bags” are distinguished from my “HODL” i.e. coins I intend to hold long term and my “moonshot” speculative assets.
What does it mean to “pull rug” and how not to get rekt
The 2020 equivalent of 2017’s “exit scam”, DeFi projects “pulling the rug” on unsuspecting victims is sadly becoming more popular as the DeFi craze and markets are heating up. There are 2 common ways this is done:
- The scam project entices people to lock their cryptocurrencies e.g. ETH into a wallet with the intent to purchase the token before it is listed. (www.focolare.org) The wallet would then be “compromised” whereby the contract address ownership would be changed and the cryptocurrencies locked in the wallet would all be withdrawn and quickly sold on exchanges.
- The scam project would mint a token and either airdrop or give a percentage of the token to some early adopters. Afterwards the scam project would try to generate hype on social media and list the project on Uniswap. Unsuspecting victims would then deposit their ETH in Uniswap in exchange for the token. After people start injecting liquidity into the Exchange, the scammer would quickly drain the liquidity from that pool, leaving holders with worthless tokens.
Here’s some of the ways to identify scams:
- Do full research on the project, check and monitor their social media. See also what other groups and people are saying about the project, and check if the claims on the project’s website are true. Also, has the project’s smart contract been audited? Is the project working with anyone reputable?
- Check if the project has actually burnt their minter key, which would prevent them from minting more tokens, withdrawing them, and rendering your tokens worthless as in the scam in 2 above.
Bear in mind that if you are the victim of a “rug pull” there is almost no way to recover your losses. So if you have any doubts about a project it is probably best to trust your instincts and not go into it. And if you do choose to put your assets into it, only put what you can afford to lose.
Oin Finance public sale delayed- you can stop spamming your F5 button now
OIN Finance aims to become a bridge between Ethereum and Ontology assets and tokens- this would mean you can trade between these 2 types of assets. One interesting potential this that by allowing the bridging of other assets from Ethereum onto Ontology, users would be able to use Ontology as a way for the exchange of assets. So users can bring assets onto Ontology chain and use Ontology to complete transactions which may make it faster and cheaper.
OIN is also a hugely popular project in China, and as we’ve seen with other projects like Polkadot, the China hype is very real. So when OIN announced it was doing a limited public sale of its token, everyone went onto their website and eagerly spammed the refresh button in the hopes of being able to sign up. However on the day of the public sale, according to OIN, they experienced a severe DDOS attack that took down their official website and registration page and were unable to resolve the issue in time.
Their rescheduled public sale will be on 31 Aug 2020 at 12:00pm (UTC). The participation instructions will only be given at that time through their social media channels. Only winners will be required to submit KYC, and each winner can only buy 7,500 OIN at $0.08 USD.
Meanwhile, be careful of fake OIN telegram channels (this is the real OIN telegram channel) which we saw pop up literally minutes after the announcement to postpone or scammers who contact you to try to sell you OIN.
Upcoming events
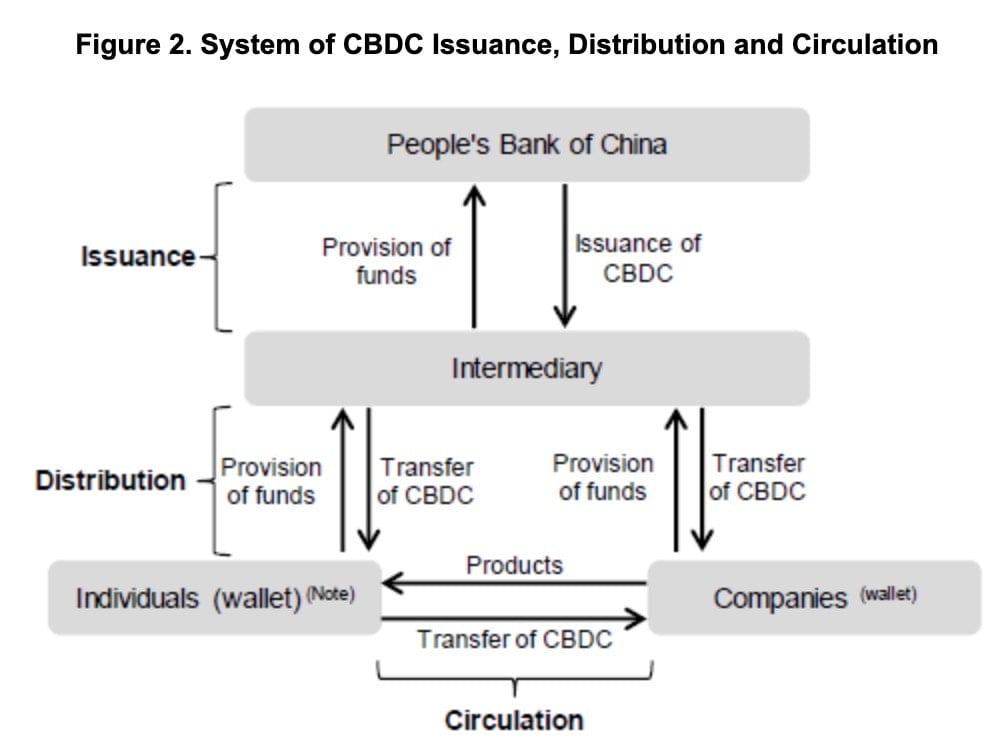
Sat 29 Aug 2020 at 12:00pm (UTC): My segment on Phoenix TV’s “一虎一席谈” (a popular hardcore debate show in China) will be broadcast. The episode discusses CBDC/ DCEP- China’s digital currency and also features fellow $YFII governance key signer Cao Yin. Note the program is in Chinese only.
31 Aug 2020 at 12:00pm (UTC): OIN Finance public sale
Tues 1 Sept 2020 at 1:00pm (UTC): Hedget token auction. Details here.
Thurs 3 Sept 2020 at 4:00pm (UTC): SKALE Network’s SKALE token will be launched and available for sale for 48 hours. However, only those who have successfully passed the KYC process will be eligible to purchase. For details, check the email from Codefi Activate.
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency trading involves significant risks and may result in the loss of your capital. You should carefully consider whether trading cryptocurrencies is right for you in light of your financial condition and ability to bear financial risks. Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile and can fluctuate widely in a short period of time. As such, trading cryptocurrencies may not be suitable for everyone. Additionally, storing cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange carries inherent risks, including the potential for loss due to hacking, exchange collapse, or other security breaches. We strongly advise that you seek independent professional advice before engaging in any cryptocurrency trading activities and carefully consider the security measures in place when choosing or storing your cryptocurrencies on a cryptocurrency exchange.










 Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) series: tutorials, guides and more
